It has been more than a century since wireless charging was first introduced, but its inclusion in devices like Apple’s new iPhone line has given it a new lease of life. Explore the technology’s inner workings and discover why it could one day be found in a wide variety of things, from houses to robots.
Some a half dozen wireless charging technologies are in use today, all of which are aimed at eliminating the need for cables to charge everything from cellphones and laptop computers to kitchen appliances, automotive engines, as well other electronic gadgets.
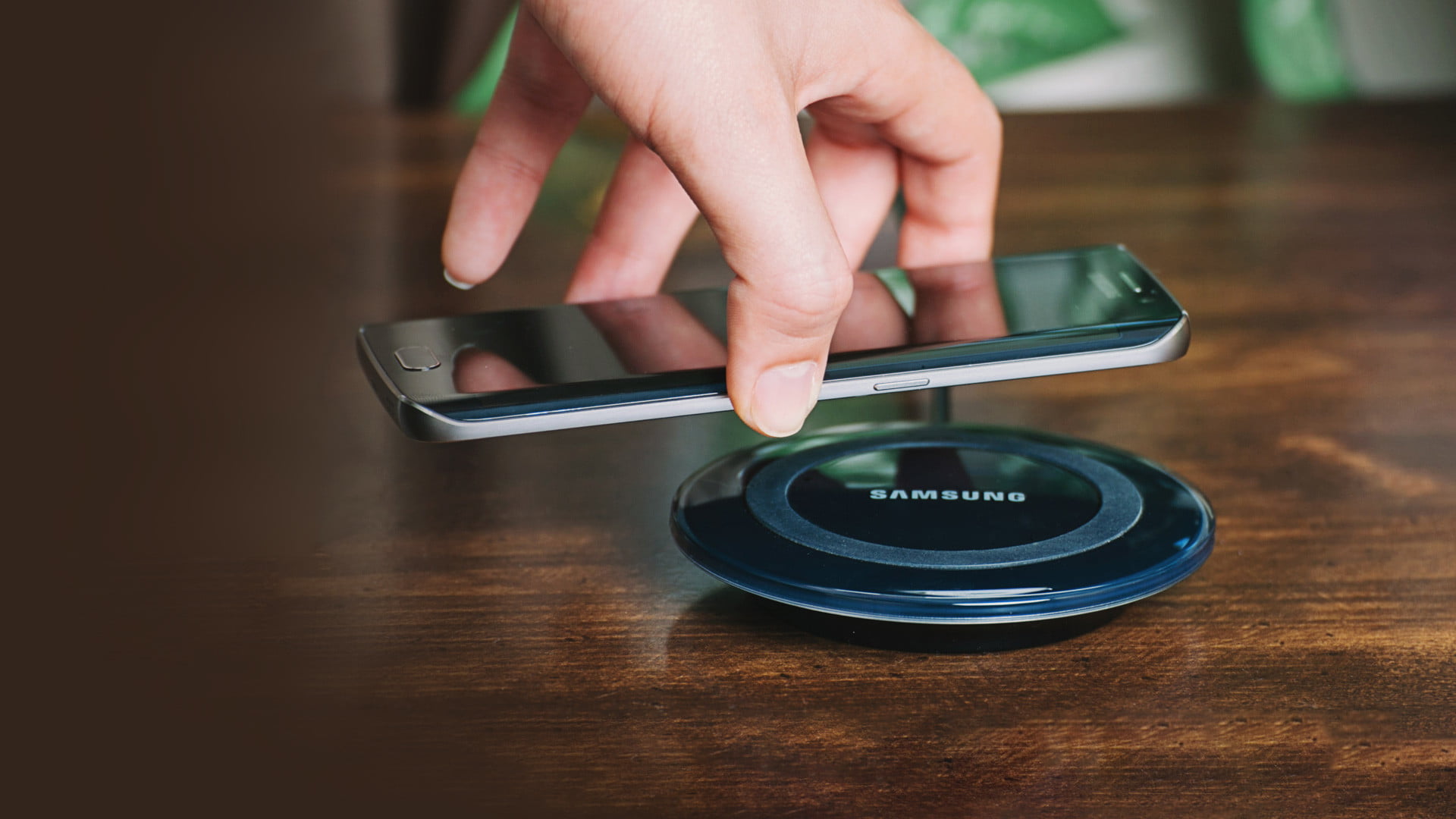

A smartphone can now be charged without the use of a charging cord, as indicated by the term “wireless charging.” According to Apple, simply placing your smartphone face up on a specific mat or tabletop will begin to charge the battery of your device, regardless of whether it’s an iPhone X, iPhone 8, Samsung Galaxy S8, or any other number of other handsets that support wireless charging, according to the company.
As a result of its promise of increased mobility and technological advancements that may one day allow tiny internet of things (IoT) devices to draw power from a charger from hundreds of feet away, wireless charging is making inroads in the healthcare, automotive, and manufacturing industries, among others.
How do you charge a device wirelessly?
Wireless charging is what you’re searching for if you don’t want to be bothered with a charging cord when charging your phone. Putting your smartphone face up on a certain mat or tabletop that supports wireless charging is all that is required to start charging its battery. Wireless charging is supported by virtually every smartphone, including the iPhone X, iPhone 8, Samsung Galaxy S8, and other models.
Inductive and non-radiative chargers that use tightly-coupled electromagnetic induction or resonant charging are available, as are chargers that use loosely-coupled or radiative electromagnetic resonant charging, which can transmit charges up to a few centimetres, and chargers that use uncoupled radio frequency (RF) wireless charging, which can trickle charge up to several hundred feet.
The same fundamental concept underlies both inductive and resonant charging methods: a time-varying magnetic field produces a current in a tightly linked wire loop.
###